Table of Contents
biomed VO Nagios
Information for biomed shifters
The biomed Nagios box is hosted and maintained by site GRIF from the French NGI. It monitors SEs, CEs and WMSs of all sites that support the VO. It is the major reference for biomed support team members in term of resources monitoring.
For monitoring results, go to Service Groups → Summary → service name (like SERVICE_SRM_V2, or SERVICE_CREAM-CE), or bookmark direct links like these:
Clicking on the SE/CE/WMS host name gives information on the scheduled downtimes (host state information section). Only critical problems (showing in red) may lead to ticket submission
A description of Nagios probes is available from the SAM wiki. Source code can also be found from the CERN Trac server or directly from the SVN repository.
A specific probe checks the status of Nagios itself, i.e. all critical processes for Nagios to run. It should be checked in case of suspicious behaviour of Nagios.
The figure below depicts important graphical elements in Nagios referring to downtimes and comments: 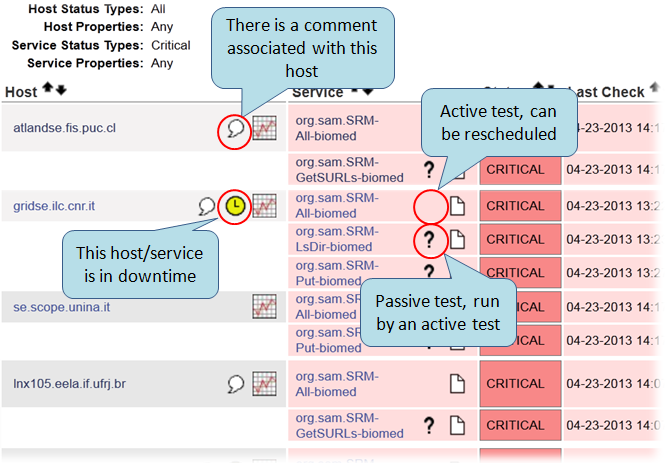
Information for administrators
Paths and configuration
Topology: a VO feed is generated every day at 23h50 by script grid04.lal.in2p3.fr:/home/fmichel/vo-feed-biomed.py. The feed is created from the status of the GRIF top BDII, an EMI BDII with expiration delay set to 24 hours.
The VO feed, biomed.xml, is then copied to a web server at 0h00 and used by Nagios to build the list of resources monitored.
Consequently, the list of monitored resources is updated every day, avoiding to monitor decommissioned resources, but also with a delay of at least 24h to monitor resources that are down for just a few hours for instance.
Paths and configuration
- Documentation: http://library.nagios.com/library/products/nagioscore/manuals/
- Configuration: /etc/nagios: nagios.cfg, services.cfg, wlcg.d/<site name>/*.cfg
- Probes path: /usr/libexec/grid-monitoring/probes/org.sam/
- Actual code of probes: /usr/lib/python2.4/site-packages/gridmetrics
Soft/Hard states vs. max_check_attempts: http://nagios.sourceforge.net/docs/nagioscore/3/en/statetypes.html
- normal_check_interval 60
- retry_check_interval 15
- max_check_attempts 4
⇒ each service is checked once an hour, if an error occurs, retry each 15 min until 4 times failed ⇒ hard state = notification, except for passive checks (passive_host_checks_are_soft=0).
Passive checks: they are initiated and performed by external applications/processes. Passive check results are submitted to Nagios for processing.
Stop/start Nagios
As root, run: service nagios restart
Changing the grid certificate
When the grid certificate of the user used to run tests is renewed once a year, copy the userkey.pem and usercert.pem files to .globus like on any UI. To do so, follow those steps:
1. Copy the pem files to the gate machine grid11.lal.in2p3.fr:
eval `ssh-agent` ssh-add gsiscp -P 2222 user*.pem grid11.lal.in2p3.fr:
2. Then log into grid11.lal.in2p3.fr and copy the pem files to the Nagios box grid4:
gsissh -AX -p 2222 grid11.lal.in2p3.fr scp user*pem fmichel@grid04.lal.in2p3.fr:/.globus
3. Then test the new pem files:
ssh fmichel@grid04.lal.in2p3.fr voms-proxy-init --voms biomed
Proxy certificate renewal
Ssh to the any UI or on Nagios server: grid04.lal.in2p3.fr
- Create a valid proxy certificate:
$ voms-proxy-init --voms biomed
- Renew the proxy
$ myproxy-init --cred_lifetime 672 --credname NagiosRetrieve-grid04.lal.in2p3.fr-biomed --pshost myproxy.grif.fr --username nagios --regex_dn_match --retrievable_by_cert "/O=GRID-FR/C=FR/O=CNRS/OU=LAL/CN=grid04.lal.in2p3.fr"
- Check the proxy:
$ myproxy-info -l nagios -s myproxy.grif.fr
- Test the proxy retrieval probe:
Ssh to the Nagios server: grid04.lal.in2p3.fr $ sudo su - nagios $ /usr/libexec/grid-monitoring/probes/hr.srce/refresh_proxy --myproxyuser nagios --cert /etc/nagios/globus/hostcert.pem --vo biomed --name NagiosRetrieve-grid04.lal.in2p3.fr-biomed -H myproxy.grif.fr --key /etc/nagios/globus/hostkey.pem -x /etc/nagios/globus/userproxy.pem-biomed